Introduction
Microservices architecture is a way of building software systems by breaking them down into small, independent services. Each service has a specific purpose and can be developed, tested, and deployed separately. And it communicates with the other services using well-defined APIs. This makes microservices systems more flexible and scalable than traditional monolithic systems, where the entire application is built as a single unit.
A microservices architecture is like a manufacturing assembly line, where each service is like a station. Each station is responsible for a specific task, such as assembling the engine, painting the car, or installing the wheels. The same is true for microservices. Each service is responsible for a specific task, such as authenticating users, processing payments, or displaying content.
Microservices architectures are more efficient, consistent, and high-quality than monolithic architectures. This is because each service is an expert in its specific task. For example, a microservice that is responsible for authenticating users is likely to be better at that than a monolithic application that has to perform all tasks, including authentication.
In contrast, a monolithic architecture is like a manufacturing environment where each station is responsible for building the entire product itself. This is a less efficient and flexible approach, as it is difficult to make changes to the product without affecting the entire assembly line.
How It Works?
Microservices architecture is a way of designing software systems where each small unit, called a microservice, has a specific job to do. Microservices are independent of each other, which means that they can be developed, deployed, and scaled separately. This makes microservices-based systems more flexible and resilient than traditional systems.
Microservices communicate with each other using messages. This allows them to be loosely coupled, which means that changes to one microservice do not affect the others. This makes microservices-based systems easier to maintain and update.
Microservices are often used in cloud-based systems, where each microservice can be run on a separate server. This makes it easy to scale the system up or down as needed.
Microservices architectures are different from traditional monolithic architectures, where the entire system is one big piece of software.
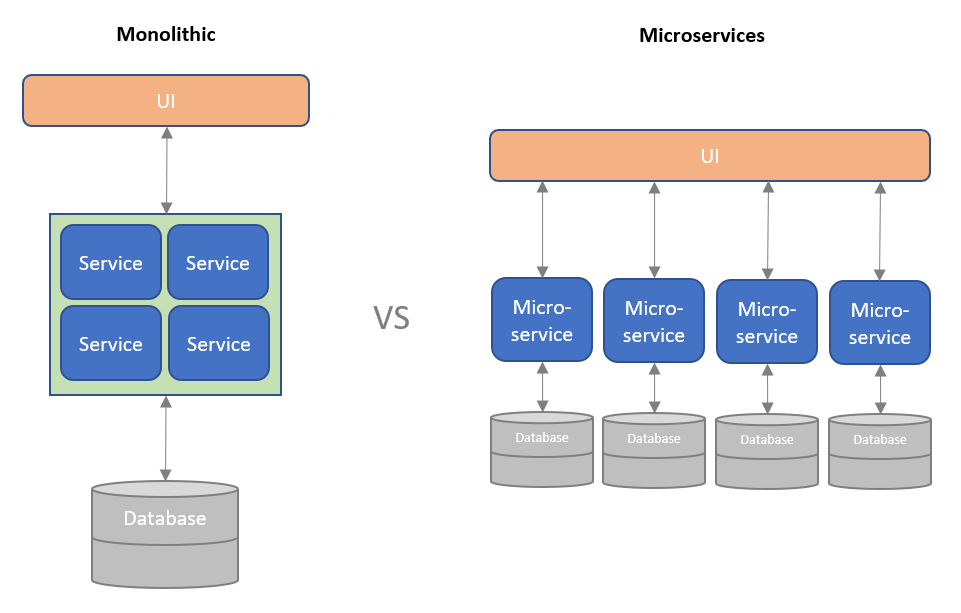
Difference Between Microservices and Monolithic Architectures
Monolithic architecture is a traditional approach to software development where the entire application is built as a single, unified unit. This means that all of the code, data, and settings for the application are tightly coupled together.
Microservices architecture is a newer approach to software development where the application is broken down into a collection of smaller, independent services. Each microservice is responsible for a specific task or function, and they communicate with each other using messages.
The key difference between monolithic and microservices architecture is that microservices are loosely coupled. This means that changes to one microservice do not affect the other microservices. This makes microservices-based systems more flexible and easier to maintain than monolithic systems.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between monolithic and microservices architecture:
| Criteria | Microservices | Monolith |
| Architecture | Distributed system with loosely coupled services | Centralized system with tightly coupled components |
| Development | Each service is developed and deployed independently | The entire system is developed and deployed as a single unit |
| Deployment | Independent deployment of each service | Deployment of the entire system as a single unit |
| Scaling | Horizontal scaling of individual services | Vertical scaling of the entire system |
| Change management | Easy to change and update individual services | Difficult to change and update the system as a whole |
| Resilience | Fault tolerance at the service level | Fault tolerance at the system level |
| Maintainability | Easier to maintain | More difficult to maintain |
| Complexity | Microservices architectures are more complex to design and implement | Monolithic architectures are simpler to design and implement |
Benefits of Microservices Architectures
Here are some of the benefits of microservices architectures:
Microservices architectures are not new, but they have become more popular in recent years. This is because microservices are a good fit for the modern world of cloud computing and continuous delivery.
Microservices Architecture Example Use Cases
Microservices architecture is a good choice for a wide range of use cases, especially those that involve complex data pipelines or machine learning. Here are some examples:
These are just a few examples of the many ways that microservices architectures can be used.
Conclusion
Microservices architecture is a modern approach to software development that offers many benefits over traditional monolithic architectures. Microservices are smaller, simpler, and more independent, which makes them easier to build, deploy, scale, and maintain. Microservices are also more resilient to failures, as a problem with one microservice is less likely to affect the other microservices in the system.
Microservices architectures are well-suited for a wide range of use cases. If you are considering building a new software system or modernizing an existing system, microservices architecture is a good option to consider.
Hitech Partners helps companies to improve technological efficiency and maximize business results.